Food Manufacturing Industry Overview and Safety Hazards
Posted by Anthony Webb on Jun 20th 2025
Food manufacturing is an extensive and vital industry for feeding animals and people worldwide. Without a thriving food industry, mankind’s numbers would slowly diminish, making food manufacturing a critical piece of infrastructure.
The industry’s importance is demonstrated in some key 2021 figures:
- In the U.S. alone, food manufacturing produced $746.5 billion in revenue
- 1.7 million people are employed in the industry
- Over 42,000 food and beverage establishments exist across the U.S.
- The industry makes up 15% of the total manufacturing shipments produced in the U.S.

Packaging Chicken on a Production Line
The good news is, based on the above data, the food manufacturing industry is thriving. However, that doesn’t mean there are no challenges in preparing final food products for consumption. Food safety is always a top concern due to the issue of potential contamination caused by either unclean plant processing facilities or improper handling and shipping to end consumers. In addition to food safety, worker safety is an essential focus at food manufacturing facilities. Workers encounter numerous workplace hazards, including sharp blades, toxic chemicals, and hazardous machinery. Overall, there are 5.1 recordable injuries for every 100 employees in food manufacturing, 43% higher than the average across all industries.
This article will provide a helpful overview of what food manufacturers do, which sub-industries exist, what specific jobs occur at manufacturing facilities, what the industry's accompanying hazards are, and recommended safety measures.
Industry Overview

What do food manufacturers do? They use machinery and employee labor to transform livestock and agricultural goods into products ready for consumption. This includes everything from processing meats and poultry to baking breads and cereals for distribution. Some companies produce the materials used by other processing plants to make products, such as syrup for beverage manufacturing companies. However, the bulk of products manufactured go to wholesalers and retailers for distribution to end consumers.
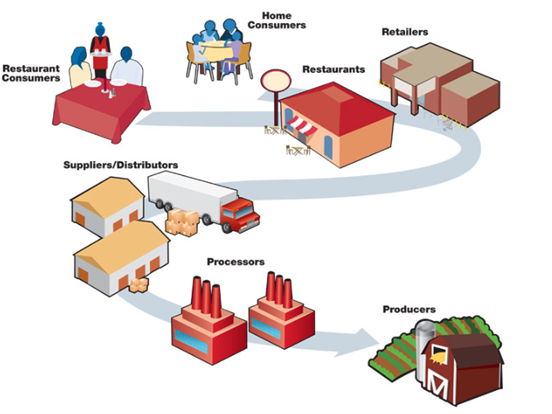
A visual aid in the long chain of food production
Within food manufacturing, numerous sub-industries make up the industry as a whole. Our next section dives into each specific sub-industry.
Sub-Industries
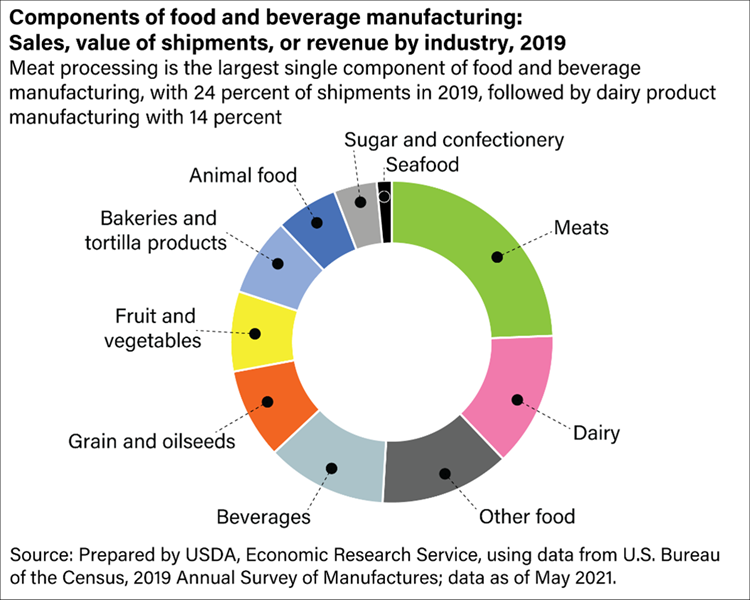
This chart shows the breakdown of subindustries within food manufacturing.
The food manufacturing industry falls under the NAICS code 311, a designation reserved for commercial food items intended for public consumption. Within the NAICS 311 category, several subindustries focus on different food types. Below is a breakdown of each subindustry and a few key companies within each sector. Before we break down each subindustry, we first list the top companies employing the most workers.
Animal Slaughtering and Processing

(NAICS 3116): This subindustry relates to meat and poultry items. Manufacturers slaughter livestock, then process and package it for consumer use. There are 538.5 million workers employed in this sector. Two of the largest companies within this sector are:
- JBS Food: the #1 beef producer in the U.S., it’s also highly ranked for pork (#2) and poultry (#2). The company focuses on food that is high-quality, fresh, easy to use, and ready for immediate sale.
- Tyson:focuses on protein products, processing 20% of the nation’s beef, pork, and chicken. Tyson provides meat for other producers and sells directly to national restaurant chains.
Bakeries and Tortillas

(NAICS 3118): This subindustry processes goods such as bread, dry pasta, cookies, crackers, flour, and tortillas. It employs 297 million workers. Two of the largest companies within this sector are:
- Bimbo Bakeries: the largest manufacturer of baked products in the world. Its goods, including sliced bread, rolls, hot dog and hamburger buns, muffins, and bagels, are staples in approximately 80% of homes in the U.S.
- Flower Foods: provides baked goods to retailers and restaurants across the country.Top brands include Nature’s Own, Wonder, and Dave’s Killer Bread.
Fruit and Vegetables

(NAICS 3114): This subindustry is responsible for processing fruits and vegetables, including fresh, canned, dried, and frozen products. There are 168 million workers employed in this sector. Three of the largest companies are:
- Kraft Heinz:the leader in fruit- and vegetable-based products, including ketchup, sauces, snacks, and baby food. The company employs more than 38,000 employees in 40 countries worldwide.
- General Mills: the top manufacturer of organic and natural foods in the U.S., including frozen fruits and vegetables.
- Campbell’s Soup: one of the top producers of canned soups and soup mixes. The company also makes snacks like crackers, chips, sauces, and juice.
Dairy Products

(NAICS 3115): This subindustry processes dairy products such as milk, condensed and evaporated milk, cheese, yogurt, and butter. There are 152 million workers employed in this sector. Two of the largest companies are:
- Nestle: the largest producer of food and drink products in the world. The company has more than 2,000 brands located in 186 countries.
- Saputo: focuses on processing milk to make a large variety of delicious cheeses and other dairy products.
Sugar and Confectionery Products

(NAICS 3113): This subindustry processes raw materials such as sugarcane, sugarbeet, and cacao to produce sugars, confections, and chocolate. It employs 72.9 million workers. Two of the largest companies within this sector are:
- Mars: the top manufacturer in the world for chocolate, chewing gum, mints, and other confections. Mars works with brands such as Dove, 3 Musketeers, Juicy Fruit, and many more.
- Hershey’s: produces chocolate bars, chocolate kisses, and syrups. It also works with other chocolate production companies, such as Reese’s, KitKat, Caramello, and Cadbury.
Grain and Oilseed Milling

(NAICS 3112): This subindustry is responsible for grinding grains and oilseeds to produce flour, cooking oils, fats, and cereals. The industry employs 61.5 million workers. Two of the largest companies within this sector are:
- Archer Daniels: in business since 1902, the company has nearly 800 facilities worldwide where grains and oilseeds transform into various products used in food, animal food, beverages, and more.
- Bunge: produces specialty oils and grains. It provides oil and fat ingredients, wheat, rice, and corn products to manufacturers, bakeries, restaurants, and other foodservice companies.
Seafood Product Preparation and Packaging

(NAICS 3117): This subindustry prepares fresh, canned, and frozen seafood products, in addition to byproducts such as oils and fats. Roughly 32 million workers are employed in this sector. Two of the largest companies are:
- Rich Products: a leader in the seafood industry. Its SeaPak brand is the country’s top-selling frozen specialty seafood.
- Trident Seafood: a family-owned company that has specialized in catching fish for three generations. Once the fish are caught, they are prepared and frozen onboard and then distributed to wholesalers, retailers, and foodservice companies.
Animal Food

(NAICS 3111): Food manufacturing includes more than just products for human consumption. This subindustry manufactures food for farm livestock (horses, pigs, cows, etc.) and household pets (cats, dogs, etc.). There are roughly 66 million workers employed in this sector. Two of the largest companies are:
- Cargill:produces feed for livestock, focusing on balanced animal nutrition. Cargill manufactures finished feed and feed ingredients, premixes, and additives for other global brands.
- Purina: specializes in quality dog food , 99% of which is made and distributed in the U.S. Purina maintains and operates its production facilities to monitor the manufacturing process and conduct quality-assurance testing.
Top Companies

Manufacturers in the above subindustries distribute products to customers, including other manufacturers, grocery stores, wholesalers, retailers, and restaurants. Below is a summary of the top 25 companies based on the total number of workers employed.
| Rank | Company | Total Employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nestle | 273,000 |
| 2 | JBS Foods USA |
233,797 |
| 3 | Cargill Inc. | 166,000 |
| 4 | Tyson Foods Inc. | 139,000 |
| 5 | Mars Inc. | 130,000 |
| 6 | Mondelez International | 80,000 |
| 7 | Smithfield Foods Inc. | 50,200 |
| 8 | Kraft Heinz Co. | 38,757 |
| 9 | Archer Daniels Midland | 38,100 |
| 10 | Pilgrim’s Pride | 35,700 |
| 11 | General Mills Inc. | 35,000 |
| 12 | Kellogg Co. | 34,000 |
| 13 | Bunge | 32,000 |
| 14 | Hormel Foods Corp. | 20,000 |
| 15 | Bimbo Bakeries | 20,000 |
| 16 | Saputo Inc. | 18,000 |
| 17 | Purina Mills | 18,000 |
| 18 | Conagra Brands Inc. | 16,500 |
| 19 | Hershey Co. | 16,140 |
| 20 | Campbell Soup Co. | 14,000 |
| 21 | Rich Products | 11,000 |
| 22 | Trident Seafoods | 9,000 |
| 23 | National Beef Packing Co. | 8,200 |
| 24 | J.M. Smucker Co. | 7,300 |
| 25 | Pinnacle Foods | 4,900 |
Jobs Requiring PPE
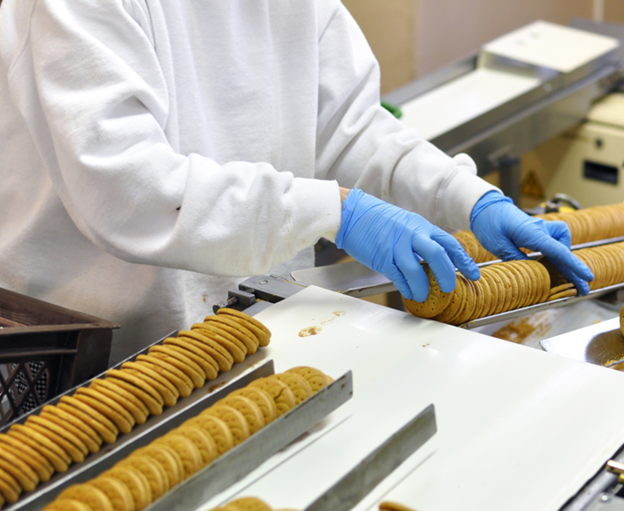

An army of workers in this industry process and prepare the foods, and all of them must be kept safe. The most common jobs in this industry are the food processing workers, including bakers, butchers, meat packers, and cooking machine operators. However, not all jobs involve directly handling food. Some food manufacturing jobs involve cleaning equipment, maintaining conveyor systems, and keeping machinery running.
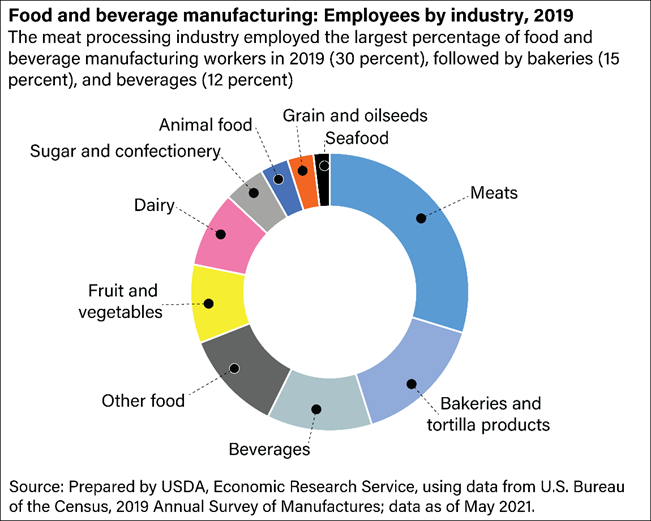
Don’t let the revenue numbers fool you: bakeries are the second largest employers in this industry.
There are many occupations within the food manufacturing industry. Below is a list of the occupations with the highest levels of employment and the activities each worker performs. Understanding these activities is crucial in determining what personal protective equipment (PPE) will need to be worn.
| Job | 2020 Employment | Core Descripton | Additional Work Activities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging and Filling Machine Operators | 149,180 | Operate the machines that prepare food products |
|
| Food Batchmakers | 122,070 | Manage equipment that mixes ingredients |
|
| Meat, Poultry, and Fish Cutters and Trimmers | 118,740 | Cut meat, poultry, or seafood, either by hand or with a hand-held device |
|
| Slaughterers and Meat Packers | 72,110 | Perform specialty tasks related to the slaughter, cutting, and packaging of meat |
|
| Packers and Packagers | 67,820 | Package the food product, usually by hand |
|
| Bakers | 57,290 | Combine and bake ingredients |
|
| Inspectors, Testers, Sorters, Samplers, and Weighers | 39,670 | Provide quality assurance by inspecting, testing, measuring, and sampling the product to make sure it's up to quality standards |
|
| Industrial Machinery Mechanics | 38,680 | Conduct routine maintenance and repairs on the manufacturing equipme |
|
| Maintenance and Repair Workers | 38,440 | Provide mechanical support and perform routine maintenance on the structure of the facility |
|
| Janitors and Cleaners | 30,060 | Clean different areas of the facility |
|
| Equipment Cleaners | 23,640 | Clean industrial machinery and other equipment |
|
| Food Cooking Machine Operators | 22,120 | Prepare food by operating cooking equipment such as pressure cookers, deep fryers, boilers, and ovens |
|
| Mixing and Blending Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders | 21,250 | Manage the machinery that mixes ingredients |
|
| Separating, Filtering, Clarifying, Precipitating, and Still Machine Operators | 12,430 | Manage the machines that sort, extract, or separate ingredients to produce a refined product |
|
| Food Preparation Workers | 11,130 | Perform duties related to food preparation other than cooking, which might include slicing deli meats, storing and wrapping food, packing food according to the customer’s orders, etc. |
|
| Graders and Sorters | 10,960 | Sort and categorize unprocessed food according to size, weight, color, or quality |
|
| Butchers and Meat Cutters | 9,210 | Prepare meat to be distributed and sold |
|
Injuries and Safety Stats

The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) shows that 82,000 total injuries occurred across the food manufacturing industry in 2020. As mentioned above, the industry is well above the injury average, and some of the subindustries, such as seafood production and animal slaughtering, have injury rates that are even higher. The table below highlights the average total recordable injuries by subindustry.
| Sub-Industry | NAICS Code | Total Recordable Injury Cases (per 100 employees) |
|---|---|---|
| Seafood product preparation and packaging | 3117 | 6.8 |
| Animal slaughtering and processing | 3116 | 6.7 |
| Fruit and vegetable preserving and specialty food manufacturing | 3114 | 4.7 |
| Dairy product manufacturing | 3115 | 4.5 |
| Sugar and confectionery product manufacturing | 3113 | 3.6 |
| Grain and oilseed milling | 3112 | 3.3 |
| Animal food manufacturing | 3111 | 3.1 |
Hazards

The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) each year provides information regarding the most common food manufacturing safety violations contributing to such high injury rates. Here are the top 10 based on the number of citations issued:
- Lockout/tagout
- Machine requirements
- Wiring methods
- Processing hazardous chemicals
- Powered industrial trucks, such as forklifts
- Mechanical power transmission, such as conveyors
- Fall protection and falling object protection
- Hazard communication
- OSHA General Duty Clause
- Respiratory protection
Many of these top 10 violations result from inadequate personal protective equipment (PPE). Proper use of PPE can protect against the dangers associated with processing hazardous chemicals, falling object, hazard communication, and the General Duty Clause. MCR Safety has PPE solutions to address each of these areas.
Violation of the General Duty Clause is the most significant citation because it’s the underlining act ensuring workplaces are free from hazards. PPE must be provided when the above hazards can't be removed and remain. In addition to the top 10 safety violations, some other noteworthy citations include noise exposure, materials handled, bloodborne pathogens, safeguards, hazardous waste operations, and eye and hand protection.
Any company that needs assistance addressing any of the above hazards should review the resources offered on the OSHA website. Here are some to check out:
PPE

The PPE worn in food manufacturing will vary depending on the work performed. Those handling sawing machines will require more protection from cuts than those handling prepared food. We break down all the PPE options MCR Safety offers the food industry below.
Work Gloves

A worker’s hands play a critical role in manufacturing food, which makes gloves one of the most important and widely used forms of PPE across the food industry. From cutting meat to handling prepared foods, hands must be protected from various workplace hazards.
Gloves also help protect the food by preventing contamination during handling. Microorganisms found on a person’s skin, including Staphylococcus aureus and pathogenic Escherichia coli, are severe risks if they contaminate food products at any point during the food preparation process.
Below are the work gloves categories we know food manufacturing facilities wear:
FDA-Approved Material

Not all gloves are created equal. Some materials used in manufacturing gloves can create hazards to food safety if they come into contact with food products. Therefore, we identify all options that are made with FDA-approved material. Workers who touch food directly should ensure they are wearing one of these options.
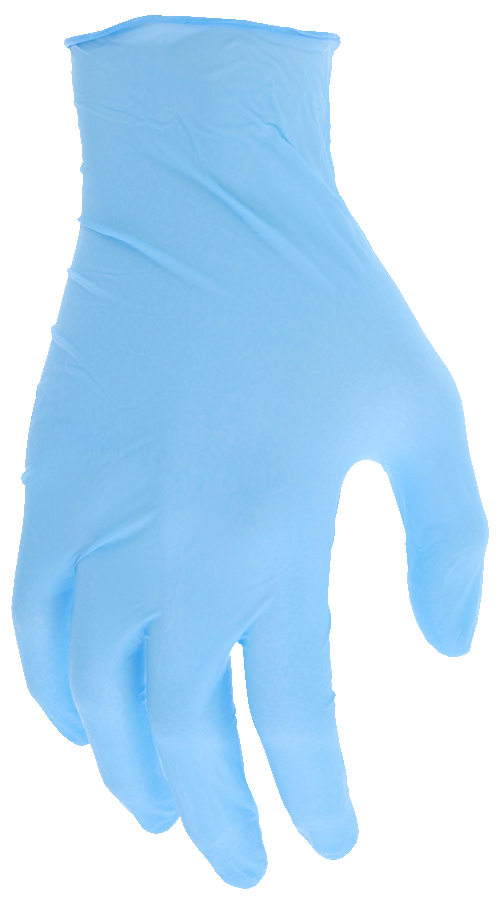
Disposable Gloves
Workers must wear disposable gloves when inspecting, preparing, and packaging ready-to-eat foods. At no time should a worker’s bare hands be exposed to food due to potential contamination concerns. Gloves also aid in preventing dead skin cells from entering food products and cover any open wounds that may be present.
Colored Disposable Gloves
Brightly colored nitrile disposable gloves provide an excellent contrast to most foods, such as meats. The bright color stands out easier against food products. Below are the top-selling styles we offer, with our premium styles offering the best protection. Check out the bright yellow!
Thick Reusable Gloves
Thicker polymer gloves with extended cuffs are used when handling raw foods and non-food items, such as boxes and garbage. Our nitrile styles are ideal for dry, wet, or oily conditions. As a tip, it makes sense to color code gloves across facilities, meaning green gloves are for garbage handling, for example.
Chemical-Resistant Gloves
Chemical sanitation is the process of cleaning equipment to ward off unwanted microorganisms using chemicals. Sterilizing vats, cleaning food preparation sinks, sanitizing handwashing lavatories, and cleaning processing machinery in manufacturing plants require chemical detergents, soaps, and disinfectants. The harsh chemicals used in this process can lead to chemical burns from direct exposure or lingering chemicals on clothing. Therefore, chemical-resistant protection is necessary for workers who engage in this type of cleaning. In addition, industrial refrigeration units use ammonia to keep food products cold, so those who may encounter it need to be protected. Finally, don’t forget about those who transport cleaners and sanitizers. They are also prone to encountering toxic materials and need to be protected.
You can quickly sort through our chemical glove options from our main online catalog or our dedicated chemical-resistant page. We encourage you to check out our permeation database to confirm that the glove you’re interested in meets your required chemical-resistant performance.
Metal-Detectable Gloves
Gloves can contaminate food by disintegrating or breaking down and entering the food production line. That’s why we offer metal-detectable options, ensuring systems can detect the presence of glove material to avoid the contamination of food products.
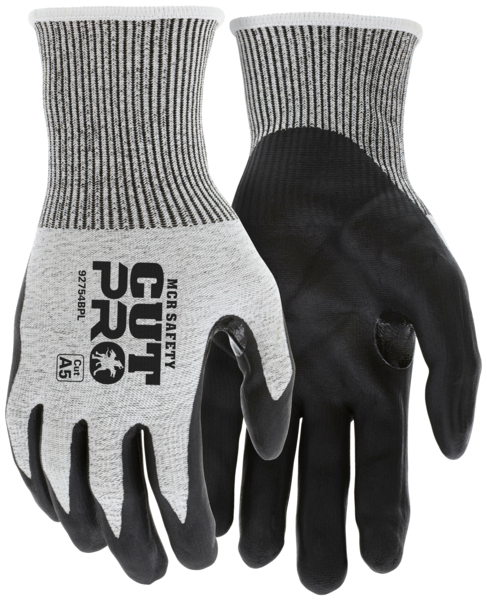
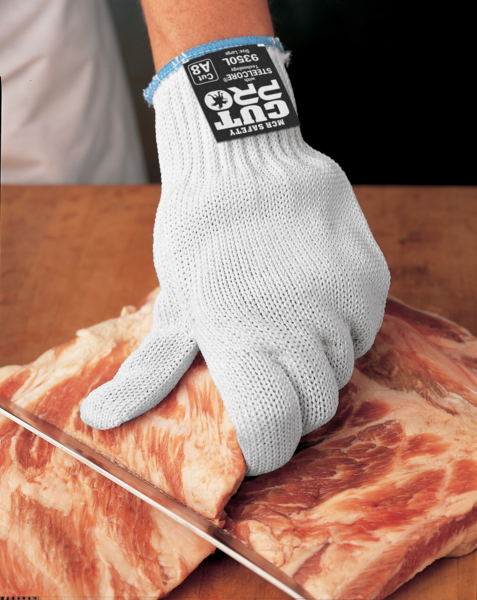
Cut-Resistant Gloves
Hands are vulnerable to severe injuries when workers cut and trim meat with knives, cleavers, meat saws, bandsaws, or other equipment. Also, equipment in a food manufacturing plant has blades, pinch points, rolling parts, and other dangers that can quickly lead to permanent damage or disfigurement. For these reasons, many food manufacturing workers will need cut-resistant gloves.
92754BP is made with FDA-approved materials and provides users with A6 cut resistance.
9350 is one of the top styles used for cutting meat. Remember, gloves such as the 9357 made with fiberglass are not intended for directly touching food.
Many users will cover a cut-resistant glove with a smooth disposable glove to waterproof the outer layer. Remember that cut-resistant gloves containing fiberglass are not recommended for contact with food. Fiberglass is known to cause injury to the intestinal tract if ingested. On our glove filtering found in the online glove catalog, we highlight the shell material as “synthetic” if it contains fiberglass If it is synthetic and used in a food processing application, it makes sense to consider other options available. You can search all of our cut-resistant glove options here. For those who need cut-resistant gloves made with FDA-approved materials, go here.
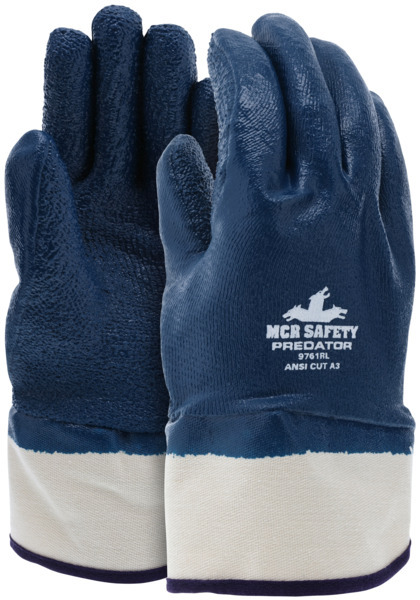
Puncture-Resistant Gloves
Workers need protection from cut and puncture hazards when handling sharp tools or sharp foods such as crustaceans or mollusks. They may also need waterproof gloves made with FDA-approved materials. Our 9761R meets both needs and provides ANSI A4 cut and ANSI 4 puncture resistance.
Heat-Resistant Gloves
Fifty-seven thousand bakers remove hot trays from ovens across this industry each day. These workers, and anyone exposed to the hot equipment used in manufacturing foods, need thermal protection. Heat and burn steam vacuums, processing cookers, and scalding water used to wash animal carcasses are all concerns for burn injuries.
Freezer Gloves
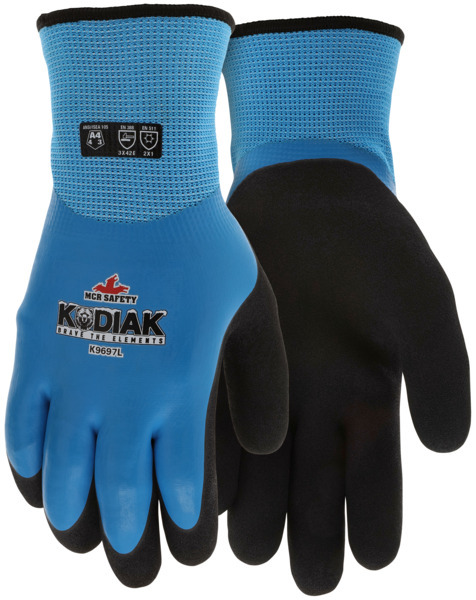
Refrigerated storage is required when warehousing food during and after production. Insulated gloves shield a worker’s hands from the cold environments found in cold rooms and freezers. You can find all our insulated styles here. We also encourage you to check out our new 9674IN option, made with Merino wool.
9674IN retains excellent flexibility, even in cold environments. Well-fitting thermal gloves allow users to grasp items easily. Throw a pair of disposable gloves over them to retain even more heat, provide a waterproof barrier, and ensure FDA-approved materials are on the outside area that may come into contact with food.
Our new K9697 is waterproof and water-resistant, ideal for areas where liquids are present.
Safety Clothing
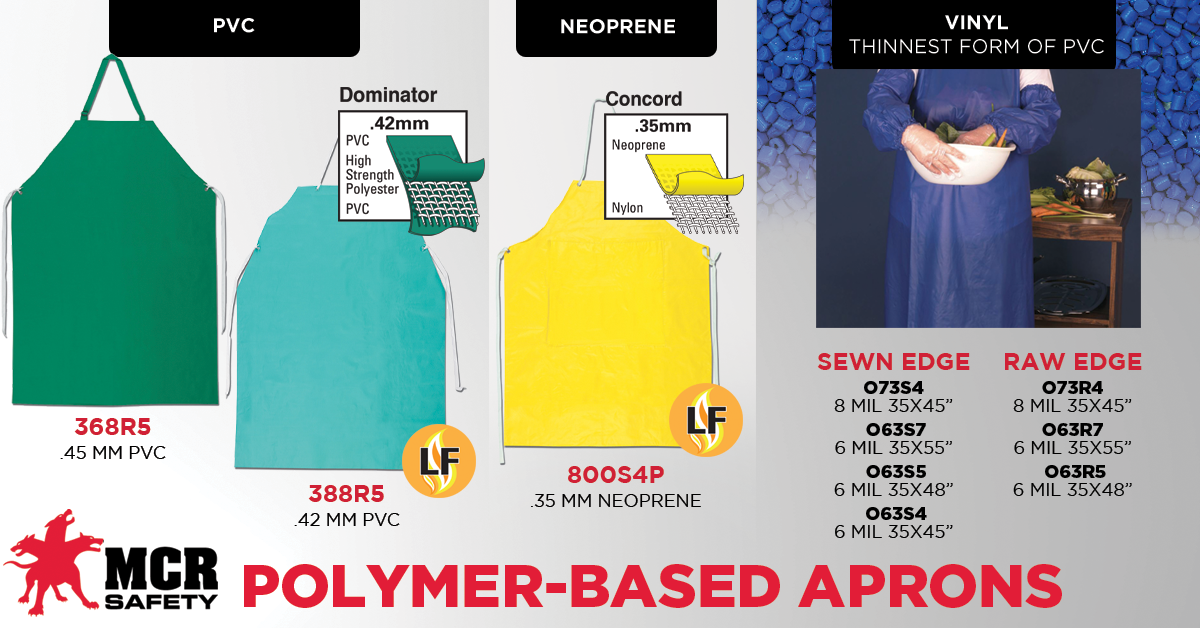
Protecting one’s body from contaminants is a primary concern for those manufacturing foods. MCR Safety provides a wide range of aprons and garments to meet the needs of this industry.
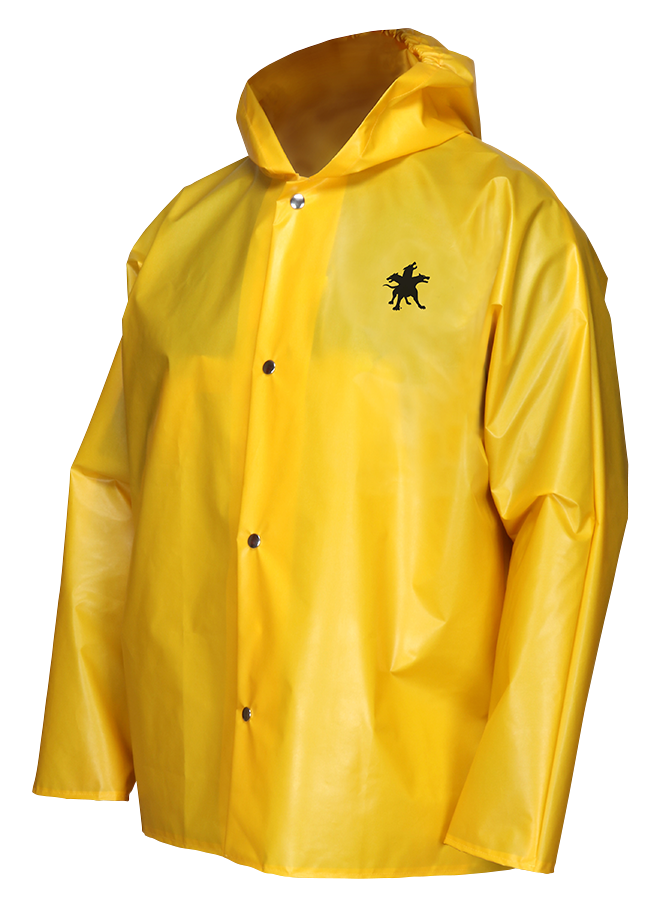
The TPU coating on the outer layer of the Navigator series jacket shown above makes it an excellent option for food processing applications since it’s resistant to many oils, fats, and greases. Plus, the material is lightweight and highly durable. The storm fly front is perfect at keeping workers protected from water and contaminants. For these reasons, this jacket is used heavily in meat packing and sanitation environments across the food industry. We also stock the 560BF, 563BF, and 568BF rain paints that complement the jacket.
Most people are familiar with using aprons in a kitchen to prepare foods. So, you can imagine how the need is even greater within largescale food processing and preparation plants. Receiving, processing, packing, and waste disposal areas all require safety clothing that protects workers from contaminants. We stock a wide range of aprons, from thin vinyl options to heavy-duty neoprene options.
Max 6 Safety Glasses
Workers in the frozen food industry are exposed to low temperatures when walking into and out of refrigerators and freezers. It's common for eye protection to fog in these fluctuating temperatures. We stock one of the largest selections of anti-fog safety glasses on the market, with our Max 6 styles offering the best anti-fog performance.
Safety Goggles
When performing any heavy-duty cleaning, it makes sense to shield your eyes entirely with goggles. Consider wearing safety goggles whenever splashes, spray, or splatter are present. The above options are the best styles we offer, and all are top-sellers.
Common Questions
What are processed foods?
- Processed food is food that has been changed in some way during preparation, including freezing, drying, canning, baking, or adding ingredients and preservatives.
How big is the food industry?
- The food industry is incredibly diverse and complex and feeds most of the world’s population. It encompasses the production, distribution, processing, preparation, preservation, transport, and packaging of food products for human and animal consumption.
Protecting Food Manufacturing Workers
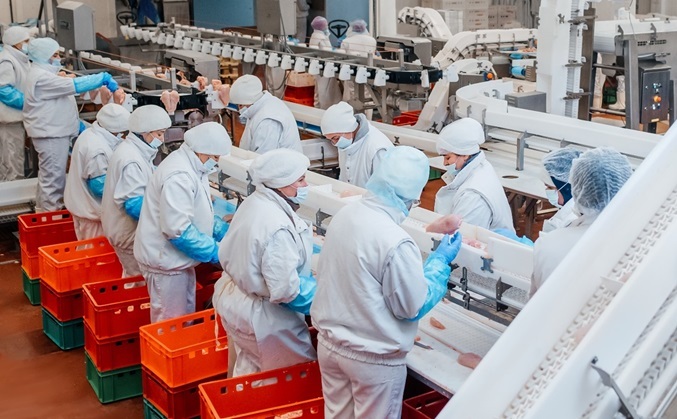

Workers in the food manufacturing industry are responsible for keeping everyone in the U.S. fed. In return, they deserve to be protected with the best safety gear available. We hope this article has illustrated how MCR Safety is doing all we can to keep these workers protected from workplace hazards. If you have any questions about the products highlighted in this article, please get in touch with us by leaving a comment below.
Click the below image to leave us comments, questions, or any concerns.
For over 45 years, MCR Safety has proven to be a world leader in gloves, glasses, and garments. Whether it's working on the production line, baking loaves of bread, or packaging food for distribution, we are there providing solutions to workplace hazards. It's all part of our commitment to protect people. No matter your industry, we have the personal protective equipment you need.
Learn more about MCR Safety by checking out our most recent video. For more information, browse our website, find a distributor, or give us a call at 800-955-6887.